Health Updates
The Vital Importance of Nutrition for Senior Citizens: Nourishing Health and Well-being
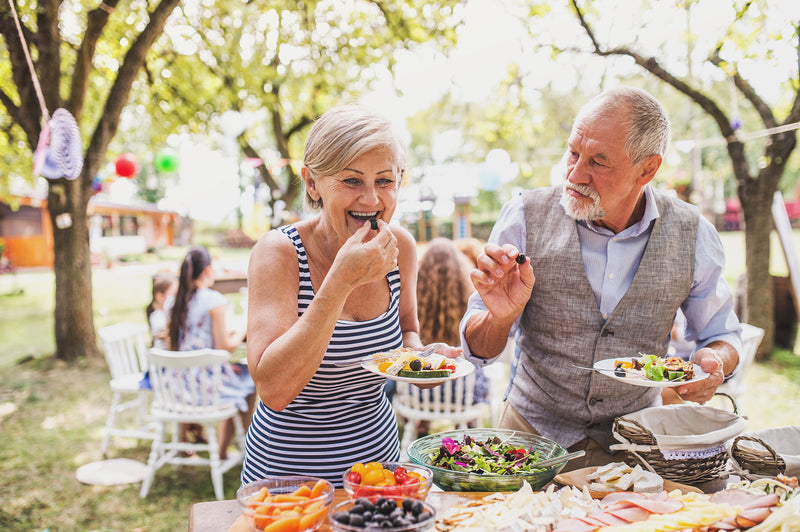

As individuals age, maintaining proper nutrition becomes increasingly vital for overall health and well-being. The nutritional needs of senior citizens differ from those of younger adults due to various factors such as changes in metabolism, reduced appetite, and age-related health conditions. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the importance of nutrition for senior citizens, discuss their unique dietary requirements, and highlight strategies to ensure optimal nutrition for this population. By understanding the significance of nutrition and implementing appropriate dietary practices, we can enhance the quality of life and promote healthy aging among seniors.
Meeting Essential Nutrient Requirements
Senior citizens require a well-balanced diet to meet their specific nutritional needs. Key nutrients of importance for seniors include:
- Protein: Adequate protein intake is crucial for maintaining muscle mass, strength, and immune function. Sources of high-quality protein include lean meats, poultry, fish, dairy products, beans, and legumes.
- Fiber: Consuming adequate fiber promotes digestive health, prevents constipation, and helps manage weight. Seniors should include whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes in their diet to meet their fiber requirements.
- Calcium and Vitamin D: These nutrients are essential for maintaining bone health and reducing the risk of osteoporosis. Dairy products, fortified plant-based milk, leafy greens, and exposure to sunlight are good sources of calcium and vitamin D.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: These beneficial fats play a role in reducing inflammation, promoting heart health, and supporting brain function. Sources include fatty fish (such as salmon and sardines), walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds.
- B vitamins: B vitamins, particularly B12, are essential for energy production, nerve function, and red blood cell formation. Seniors may require supplementation or incorporate fortified foods, lean meats, fish, and dairy products into their diet.
Managing Caloric Intake and Weight
As metabolism slows down with age, senior citizens often experience a decrease in calorie needs. However, it is crucial to ensure that caloric intake remains appropriate for maintaining a healthy weight and meeting nutritional requirements. Factors such as physical activity levels, muscle mass, and underlying health conditions should be considered when determining caloric needs. Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance in this regard.
Additionally, seniors should be mindful of maintaining a healthy body weight. Obesity in older adults can increase the risk of chronic diseases, while being underweight may lead to nutritional deficiencies and impaired immune function. A balanced diet, portion control, and regular physical activity contribute to weight management and overall health.
Hydration and Fluid Intake
Proper hydration is essential for seniors, as they may experience a decreased sense of thirst and an increased risk of dehydration. Dehydration can lead to numerous health issues, including urinary tract infections, constipation, and impaired cognitive function. Encouraging seniors to drink fluids regularly, even if they do not feel thirsty, can help prevent dehydration. Water, herbal teas, soups, and fruits with high water content (such as melons and cucumbers) are excellent choices for maintaining hydration levels.
Addressing Common Nutritional Challenges
Senior citizens may face specific nutritional challenges that require attention and tailored strategies. Some common issues include:
- Loss of appetite: Reduced sense of taste and smell, medication side effects, and age-related changes can lead to decreased appetite. To combat this, meals should be made visually appealing, and smaller, frequent meals and snacks can be incorporated to ensure adequate nutrient intake.
- Dental and oral health issues: Dental problems, ill-fitting dentures, and difficulty chewing can hinder proper nutrition. Soft, easy-to-chew foods, pureed or mashed options, and dental check-ups are important for maintaining oral health and optimizing nutrient absorption.
- Medication and nutrient interactions: Some medications can affect nutrient absorption or metabolism. Seniors should consult healthcare professionals or pharmacists to understand potential interactions and consider appropriate dietary modifications or nutrient supplementation.
- Limited mobility or chronic conditions: Mobility issues or chronic conditions may require modifications to meal preparation and shopping. Home meal delivery services, grocery delivery, or assistance from caregivers can help ensure access to nutritious meals.
Social and Emotional Aspects of Nutrition
Nutrition goes beyond the physical aspects and encompasses social and emotional well-being. Seniors may experience loneliness, depression, or social isolation, which can impact their appetite and overall dietary habits. Encouraging communal meals, participating in social activities, and fostering a supportive environment can promote healthy eating habits and enhance the enjoyment of meals.
Nutrition plays a critical role in the health, vitality, and well-being of senior citizens. Meeting the specific dietary needs of older adults is crucial for preventing age-related diseases, maintaining muscle mass, supporting cognitive function, and promoting overall quality of life. By focusing on a well-balanced diet, managing caloric intake, staying hydrated, addressing common nutritional challenges, and considering the social and emotional aspects of nutrition, seniors can optimize their health and enjoy the benefits of healthy aging. Consulting with healthcare professionals and registered dietitians can provide personalized guidance to ensure that seniors receive the necessary nutrients for a fulfilling and nourishing lifestyle in their golden years.